Can you imagine a world without banking? I can’t. Banking is an indispensable part of our modern society. Even in the situation where cash is the king, banking services invariably form a core fabric of how most economies function. However, Banks are conservative, steeped in tradition and run-on legacy infrastructure, making it somewhat difficult to respond to customers’ changing needs and offer radical, innovative banking services.
Advancements in new digital technologies has given rise to a type of bank known as a Neo Bank. The rapid growth of these alternatives to traditional banking has led to a key question; do we still need these age-old brick and mortar-based banks and can they survive over time.
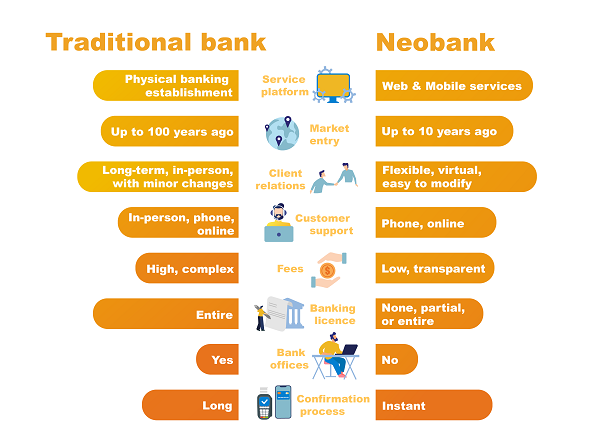
Neobanks or “challenger banks” are a new generation of Financial Technology (FinTech), mostly start-ups offering digital-first or digital-only banking services with no minimum balance requirement, no in person visits to a branch, faster banking processing time, transparent fees, low fees and sometimes no-fee services.
They are set up to challenge the status quo by providing banking solutions hitherto the preserve of traditional banks and going beyond that, add value. For example, they rely exclusively on mobile banking apps and online platforms without any physical offices or branches. Their business model is different from a traditional bank; therefore, their revenue sources do not depend on the conventional banking fee-earning structure. For example, they earn revenue from fees paid by merchants when their clients make payments rather than charging clients for services. Also, they have reduced cost of operations since they have low staff numbers and use technology such as chatbots or online-only customer services instead of call centres manned by humans.
Read also: Ghana on track to introduce E-Cedi – BoG boss
There are two types of Neobanks; full-stack Neobank and front end focused Neobanks. The full stack Neobank as the name implies is a standalone digital operation duly licensed as such. In contrast, the front end focused Neobanks is also known as “hybrids” and do not have a license to operate. Rather, they partner with a traditional bank to offer their services. In this case, the Neobank is not an opponent to the traditional bank since they work hand in hand to deliver innovative banking services. It must be pointed out there is a third type, known as a digital bank which is a competitive response to the growing influence of Neobanks; in this case, traditional banks work to develop a digital-only delivery mechanism to ensure it is attractive to its clients who may want to leave them for Neobanks.
Neobanks come with numerous advantages such as cost-effective transactions, no fees for withdrawal, lower interest rates, convenience, and the ability to access banking services anywhere, 24/7 in real-time. Designed to rely heavily on technology with minimum or no human intervention which reduces transaction errors, and are set up for our data-driven information and knowledge economy.
However, these Neobanks come with some challenges, such as lack of regulations meaning low or no protection for clients when they go bust, persons with low or no technology know-how and access cannot access their services since they do not have physical branches like traditional banks. Moreover, some of these banks have very limited services since they focus on basic savings and withdrawals and may not be able to offer some category of loans, especially mortgage or high ticketed business loans, due to the relatively small size of their balance sheet. Not all the Neobanks are successful since some of them, despite their good intentions and disruptive innovations, cannot compete with traditional banks whose history dates back centuries.
That said, Neobanks are here to stay; their disruptive impact on banking is now established, and they are growing at the speed of light. A website that tracks Neobanks, neobanks.app reported over 247 Neobanks globally as of January 2022, with 13 banks located in Africa & the Middle East. Currently, Ghana does not have a Neobank. The market for Neobanking is growing, with a current global market size valued at USD 34.77 billion in 2020 and an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected at 47.7% from 2021 to 2028. ()
In conclusion, Neobanks are radically changing the face of banking. Traditional banks will do well not to rest on their oars but work assiduously to reinvent themselves. At the end of the day, customers will benefit since the banking space’s disruption will ultimately lead to customer-centric services at competitive prices.
Source: Kwami Ahiabenu
Technology Innovations Consultant
E-mail: kwami@mangokope.com